In a new and developing space, there is bound to be a lot of noise.
” and in “The Greatest Game.”
A conflict needs to be resolved at a system level:
- Exponentially increasing efficiency driven by technological progress requires a currency that allows for deflation (bitcoin). We get more for less work.
- The existing fiat monetary system requires inflation and consequently, it needs manipulation to remain viable. We get less for more work.
Because the existing system is credit based, it cannot allow ongoing deflation without complete collapse (because the credit would be wiped out and the credit is the system). Society would never vote to have its entire way of living collapse. Which means a paradox exists where society will always eventually insist on manipulated “growth” for fear of the consequences of collapse, and that manipulated growth is the primary source of the problems that society is dealing with — including environmental damage.
Ultimately, this is because instead of allowing prices to fall (and society to gain time and freedom) with increasing productivity, it presupposes that we can “grow” forever. And the growth itself presupposes that money can be created out of thin air to achieve it. This “growth” for more jobs to be able to pay the bills, to pay for higher prices, which are manipulated higher in the first place keeps society on a hamster wheel unable to see that it is the system itself with its embedded growth obligation to service unpayable debt that is responsible for all the pain. It gets worse — from the existing system every innovation lowering price or saving time in the future must be offset with more manipulation of currency to keep the existing monetary scheme going. Energy itself provides a good example. It is not like there hasn’t been an abundance of technology deployed into the exploration, production, transportation and development of new energy sources. When you realize that the primary reason (increasing demand is important, too) energy prices have risen against new energy coming online and efficiency gains of existing energy sources, is that they must rise to support the existing credit system, you also realize there is no way out from the system.
Beyond the environmental problem being unsolvable from the existing system, Bitcoin provides a path to a Kardashev type 1 planet where we harness all the energy that can reach earth from the sun.
It does so because it provides a positive economic incentive in a transition to abundant energy. From the perspective of supply and demand, Bitcoin’s high energy cost to secure the network is a feature because an economic incentive is created that is both natural and positive to build out energy abundance. Energy is the number one driver of profitability in Bitcoin mining, meaning that low-cost energy is required for profits. A bitcoin miner cannot remain profitable by paying for energy at rates that a retail customer will, so it doesn’t compete with that energy.
Instead, it unleashes the same free market behavior in energy production and utilization. Namely searching for lower cost or stranded energy. By doing so, it provides a floor price for energy and a way to allocate capital to investments that would otherwise not be made. Those new energy investments, along with renewables, allow regions that were once cut off from the world due to a lack of reliable energy to build wealth and energy independence. The constant competition to find lower costs in energy and/or to use the heat provided from Bitcoin mining for other commercial uses such as heating greenhouses or commercial buildings unleashes a wave of entrepreneurial talent onto the challenge of energy utilization. All by way of free market competition to ensure a reliable abundance of energy and utilization.
It should be obvious to most observers by now that energy is more important in our lives than the amount of printed paper notes or digital representations of those notes. Printing more paper or digital units only creates additional energy scarcity. Energy supersedes dollars because without energy, there is no economy.
Bitcoin’s tie to energy for security and its corresponding positive effect on real growth and energy abundance is then perhaps its most under-appreciated feature (and one that the mainstream press has completely backwards).
This excerpt from Gigi (@dergigi) provides a novel way of understanding how energy protects the network:
“Anything that doesn’t have any real cost—cost that is immediately obvious and can be verified by anyone at a glance—can be trivially forged or simply made up. In the words of Hugo Nguyen: ‘By attaching energy to a block, we give it ‘form’, allowing it to have real weight & consequences in the physical world.’
“If we remove this energy, let’s say by moving from miners to signers, we reintroduce trusted third parties into the equation, which removes the tie to physical reality that makes the past self-evident.
“It is this energy, this weight, that protects the public ledger. By bringing this unlikely information into existence, miners create a transparent force-field around past transactions, securing everyone’s value in the process—including their own—without any use of private information.
“It is this energy, this weight, that protects the public ledger. By bringing this unlikely information into existence, miners create a transparent force-field around past transactions, securing everyone’s value in the process—including their own—without any use of private information.
“Here comes the part that is tricky to understand: the value that is protected is not only value in the monetary sense, but the very moral value of the integrity of the system. By extending the honest chain with the most work, miners choose to act honestly, protecting the very rules that everyone agrees to. In turn, they are rewarded monetarily by the collective that is the network.”
2. Decentralization
There are two major design choices that lead to the ongoing decentralization of Bitcoin:
1. First is the nature of proof of work in solving the Byzantine generals problem. Importantly, it is a discovery that cannot be solved again. It can be copied which sets up its own challenges, or it can be changed to try to solve it in a different manner. But, because of general relativity, changing it cannot solve the problem without introducing an oracle and centralization. Let’s dive into each of these:
a. A copy by necessity isn’t the longest chain because it must start later than Bitcoin which has the most proof of work protecting its history. The longest blockchain, by definition, is the one with the most trust. Therefore, a copy cannot have the same security or trust. Which begs the question, what utility would the new copy of Bitcoin provide that wouldn’t be better achieved through utilizing the most trusted and secure chain? Or how would a new chain without utility gain enough traction to compete with Bitcoin, while at the same time Bitcoin was exponentially increasing its security and hash rate because of its trust?
b. There is no such thing as universal time. Einstein’s theory of general relativity says the way we experience time is from our point of view. Time is relative to us — where we are. Depending on orbits, this “time” difference from our point of view on earth to Mars is between four minutes and 24 minutes. This same time difference occurs on earth as well but in such small intervals that we don’t notice it in our daily lives. The fact that we do not notice them, doesn’t change the fact that these small time differences exist. When computer systems are searching for cryptographic keys to prove they found the next block and won the prize, these small differences in time between different regions become critically important. Two Bitcoin miners on different sides of the world could solve the cryptography at exactly the same “time” because of these small variations and both be correct. It is not just theoretical, it has happened numerous times on the Bitcoin protocol and the way it is solved is, again, the longest chain, or most trust wins. For a period of 10 minutes then, or until the next block is mined, these two chains can both be valid until the next block is mined and the nodes confirm the longest chain. Miners choose which block they believe is valid and as 51% of them choose the valid block, the other miners move to the longest chain. It is a waste of energy and resources to mine on top of an orphaned block. Again, the longest chain is the one with the most trust.
Because of this discovery that ties energy and proof of work together, there exists only one other way to solve the time problem. This involves introducing a “trusted” agent or oracle that defines the “rules” and then chooses which transactions are valid (what transaction came first). But once an oracle is introduced to solve the problem, trust is placed in the oracle, the rules can change and decentralization is lost.
Bitcoin, through proof of work, is the only way to solve the problem. As Neil Degrasse Tyson points out, “After the laws of physics, everything else is an opinion.”
2. The second design choice that keeps Bitcoin decentralized is the size of the block. Sacrificing additional block size on Layer 1 of Bitcoin meant a lower number of transactions per 10 minute block and/or less room for smart contracts in the underlying code. By keeping the block size small, the tens of thousands of full node operators around the world are the true rule enforcers of the network. (Tomer Strolight gives a great firsthand account of this power in the hands of the node operators here.)
Therefore, while miners compete as economic actors to secure the network, they are held in check by nodes (open to anyone to easily set up and run) who confirm the transactions. These full nodes each have an entire history of the blockchain and confirm each of its transactions. Because block size is kept small, it means that these nodes are very economical to run in hardware and energy costs, which in turn leads to more nodes or participants validating the system (decentralization).
By adding additional information or space to the blockchain on Layer 1, the cost in energy and compute power to secure the network explodes, and in turn leads to only the most powerful or wealthy having enough money to run nodes, which in turn controls the decisions, i.e., centralization. The Blocksize Wars starting in 2015 to 2019 were fought over this key issue with many of the most powerful Bitcoin proponents at the time favoring a rule change that would bring more functionality to Layer 1, but in turn would give them more control in the form of centralization. Bitcoin hard forked over this fight with new code representing the new rules. Unlike soft forks which are agreed to by the miners and nodes and are backwards compatible, hard forks create a new chain. For example, if you owned bitcoin prior to August 1, 2017, and a hard fork to Bitcoin Cash occured, you would own coins in both chains. You could then elect to sell one of them in favor of the other or keep both. Below is a snapshot of what the market determines as value in both coins:
Market capitalization of Bitcoin as of August 6, 2022: $443 billion
Market capitalization of Bitcoin Cash as of August 6, 2022: $2.7 billion
The price discrepancy of the fork demonstrates again that while anyone can change the rules to offer a different coin, the longest chain with the most proof of work has the most trust, and is valued higher by market participants as a result. Decentralization is a big part of this trust.
3. Scalability
As reinforced throughout this article, the design choices that led to decentralization and security which itself wasn’t possible before Bitcoin, also led to design choices that lacked scalability. It is here that much of the conflict and confusion in blockchains originate. From a human nature perspective, it is easy to see that there would be conflicts, some users that wanted to build more in terms of scaling or differentiation on top of Bitcoin and felt blocked by its slow and methodical consensus of nodes protecting the ecosystem. They then decided to create their own blockchains with differentiation and tried to convince others that the new blockchains were better in some way. While many were/are complete fraudsters looking to make a quick buck on the back of ignorance, some may not have even been aware of the long-term implications of their design decisions in creating blockchains that must fail — either due to one, centralization and lack of economic incentives, or two, security vulnerabilities. And once created, there was no way out but to admit failure, or to keep changing while promising to solve the paradox at some point in the future.
A Different Way To Scale
Protocols scale in layers. Scaling Bitcoin in layers provides a way to retain security and decentralization of Layer 1, but also gain scalability in the second or third layers instead of sacrificing the first, similar to the layers that form the building blocks of the internet and ultimately the products that you use every day. Each of the different protocols operate only at that layer. This abstraction ensures that each layer is self-contained, only needing to know how to interface with the layer above and below it, which simplifies design and flexibility without sacrificing what another layer provides. This short YouTube video provides a good overview of the network protocol layers of the TCP-IP layered model.
Because of the misunderstanding that protocols scale in layers, and the overall noise in the market, innovations like Lightning that allow Bitcoin to scale would be largely dismissed by an audience that saw Bitcoin as slow-moving, old technology, uncompromising in its security and decentralization.
This would provide an asymmetric opportunity for the nations, entrepreneurs, capital and public who took time to understand what was happening in the ecosystem versus those who dismissed it.
I believe that we are at that inflection point where technologies such as Lightning, Fedimint, Taro and others will usher in a wave of innovation in the space. I also believe although it is still in its infancy, Bitcoin and the protocol are unstoppable.
Below is a chart of Lightning adoption since inception:
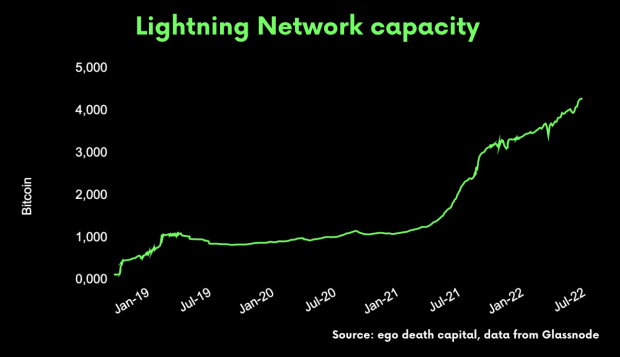
From Lyn Alden’s recent masterpiece on The Lightning Network:
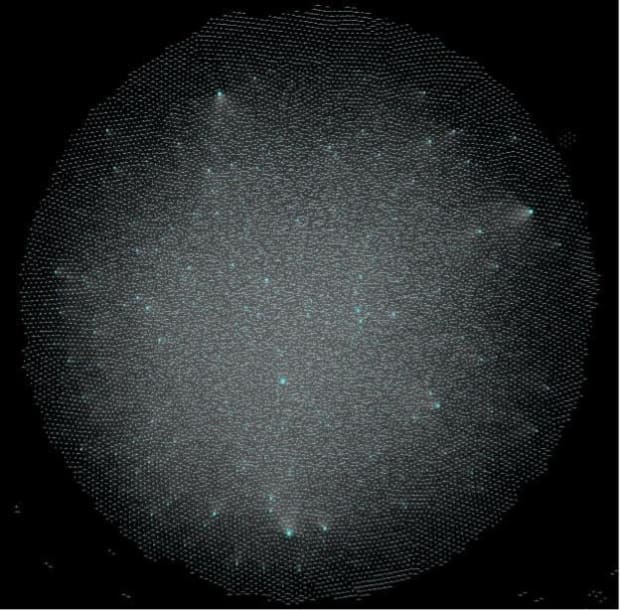
“Imagine a global system with a massive number of interconnected nodes. Anyone can enter the network with a new node and start creating channels. Alternatively, many custodial services also gives their account-holders access to the network through their nodes and channels.
“Here’s a visualization of the public Lightning network at the moment. It’s a growing network of interconnected nodes connected by payment channels, with those bigger dots representing particularly well-connected nodes:”
It is early, and not everything will work out as planned, but each success scaling in layers reinforces and brings more talent and capital to the ecosystem. Some of these pieces of the puzzle (like Lightning, Taro and Fedimint) will work together in ways not yet completely understood — accelerating adoption, all of them will build upon a Layer 1 foundation that is rock solid. In doing so, many of the long-term “use cases” of alternative coins will disappear and one by one, they will fail.
The Bitcoin protocol, scaling in layers, will provide a base layer that merges a new peer-to-peer internet and money natively within it. This will form a completely secure, open to anyone, integral foundation for technology more broadly. Like the dawn of the internet, but this time decentralized and secure, ensuring with its design a hopeful path for humanity where the natural abundance gained through technology is broadly distributed to society instead of being consolidated in the hands of a few. Regulators in certain nations could try to slow or stop it, but in doing so, they would be making a grave mistake, analogous to shutting down the internet from their citizens and blocking the innovation that came with it. It wouldn’t stop the innovation but would instead ensure that the innovation, and value derived from that innovation moved to other nations. Over time, people will realize that instead of pricing bitcoin “from the system” that they live in today, bitcoin will price everything in that system.
There will be incredible successes, failures, and learnings. Most importantly though, there will be enduring value to society that comes on top of a solid foundation that is incorruptible by a small group of people — decentralized and secure by its design. That emergent system, launched to the world by Nakamoto in 2009, changes everything.
Some leading thinkers in space and their work:
Troy Cross and Kyn Urso
This is a guest post by Jeff Booth. Opinions expressed are entirely their own and do not necessarily reflect those of BTC Inc or Bitcoin Magazine.